What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on creating solutions that imitate human thinking and behavior. Such systems can perform various tasks, such as understanding speech, recognizing patterns, or making decisions. Chatbots (like ChatGPT), autonomous vehicles, or smart assistants such as Alexa or Siri are just some examples of AI systems we hear about today. In this article, we’ll explore the real-world applications of artificial intelligence in more detail.
What Can Artificial Intelligence Do?
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the way we do business, communicate, and interact with the world. By combining the ability to analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and generate new content, AI enables the creation of cohesive, multi-dimensional solutions tailored to users’ and market needs.
One of the key areas where AI plays a significant role is in prediction and data analysis. With advanced machine learning algorithms, AI can detect hidden patterns in large datasets, enabling highly accurate forecasting of future events. For example, analyzing meteorological data from various sources allows AI to forecast weather conditions, predicting rainfall, temperature, and other phenomena. This predictive capability is also invaluable in business—AI analyzes sales, market, and operational data to support better strategic decision-making, leading to optimized processes and resource allocation.
Another major area is image and sound recognition, which forms the foundation of AI applications in manufacturing and automotive sectors. AI-powered systems can accurately identify defects in parts on production lines, automating quality control and allowing immediate corrective actions. This makes production more efficient and reduces waste. Similar applications exist in medicine, where AI analyzes medical images to detect early stages of disease, significantly improving chances of effective treatment.
A key aspect of AI is also natural language processing (NLP), which enables systems to understand and generate human language. This allows for automatic and seamless interaction with users. In customer service, AI answers questions and resolves issues via chatbots, eliminating the need for human intervention in routine queries and ensuring 24/7 availability. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also enhances operational efficiency.
AI is also advancing in content generation—from text to images, music, and video. In marketing and media, this ability is widely used to create personalized campaigns and content. For instance, AI algorithms can generate ad copy based on user preferences, compose music inspired by popular styles, or write articles. As AI becomes more advanced, the line between human and machine-generated content is beginning to blur.
All of these capabilities support the idea of personalized services. AI analyzes user behavior, such as purchase or browsing history, to deliver product and service recommendations with near-perfect precision. As a result, users receive offers that match their unique needs, increasing satisfaction and customer loyalty, while bringing real business value.
In summary, AI functions as a cohesive, integrated system supporting process optimization, service quality, and customer satisfaction—from data analysis, image recognition, and language processing to personalized experiences. AI technologies are forming the foundation for future solutions that will not only be more efficient but also better suited to the dynamic needs of users and businesses.
How Do Industry Leaders Use AI?
Tesla uses advanced AI-supported vision systems in its factories to monitor part quality. High-resolution cameras capture images at various stages of production, and AI algorithms analyze them to detect defects. This allows Tesla to quickly identify and fix issues, improving quality and reducing faulty components.
Siemens applies AI to predict equipment failures by analyzing sensor data and maintenance records. This allows them to anticipate breakdowns and optimize production processes.
Amazon employs humanoid robots in its warehouses to move bins from shelves to conveyors. This speeds up work, improves accuracy, reduces errors and accidents, and allows 24/7 operations, cutting costs.
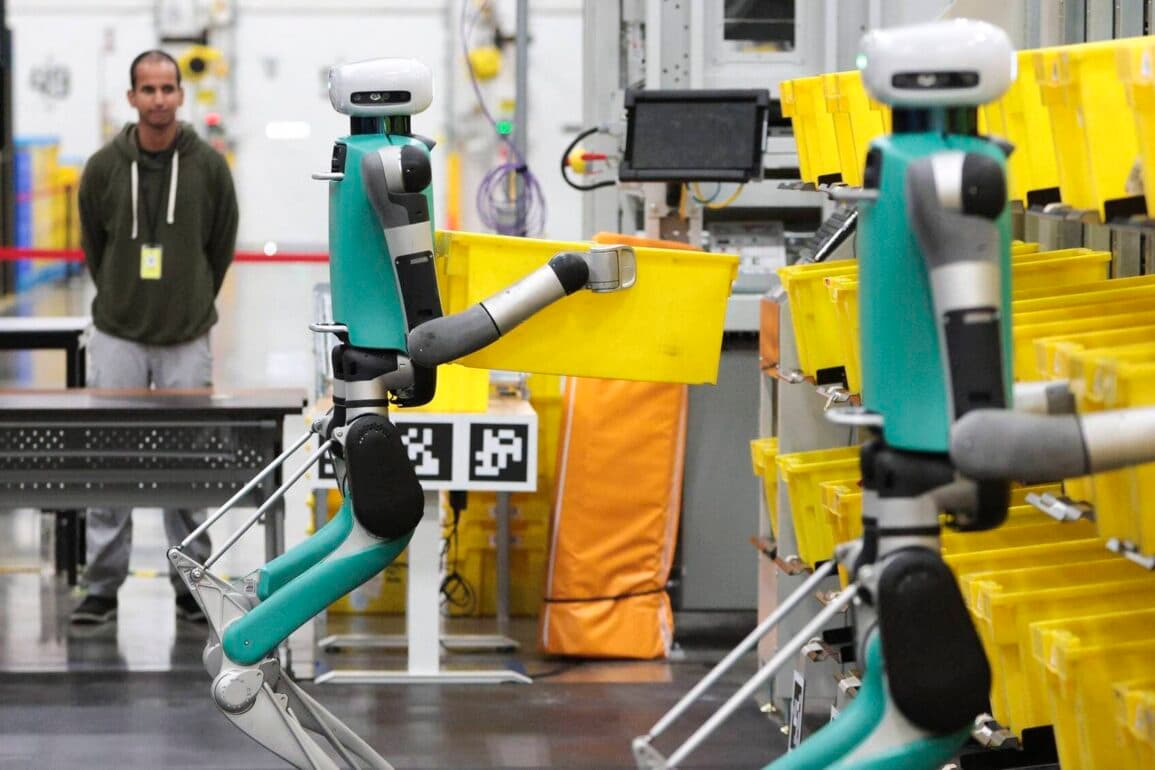

LG uses AI to improve production in its factories (e.g., LG Smart Park). AI systems monitor and analyze processes in real time, enabling faster issue detection and better resource management. This reduces downtime and increases efficiency, making their factories an industry benchmark.
Procter & Gamble leverages AI to optimize its global supply chain by analyzing data from raw materials to final delivery, helping reduce costs and better respond to market changes.
Ford uses collaborative robots (cobots) on assembly lines to assist workers with heavy and complex parts, improving ergonomics and allowing workers to focus on more advanced tasks.
Google Health developed an AI system that analyzes mammograms for breast cancer detection. In clinical trials, the system outperformed radiologists in accuracy, reducing both false negatives and false positives.
Energy Sector Applications
Hitachi uses AI to optimize energy grid management for more efficient distribution. It monitors and analyzes real-time data to respond instantly to demand changes or failures. AI also supports renewable energy integration, stabilizing supply despite the variability of solar and wind sources.
Energy production optimization: AI analyzes weather, consumption, and equipment data to maximize power plant efficiency and reduce costs, especially in wind and solar energy plants.
Zarządzanie popytem i podażą: Systemy AI mogą prognozować wzorce zużycia energii oraz automatycznie dostosowywać podaż energii, aby unikać przeciążeń i zwiększać efektywność sieci energetycznych. To umożliwia również bardziej precyzyjne planowanie konserwacji i interwencji technicznych.
Demand-supply management: AI systems forecast energy usage patterns and adjust supply automatically, improving grid efficiency and allowing precise planning of maintenance or interventions.
Network operation automation: AI automates grid management decisions, balancing loads and integrating renewables more effectively.
Consumption forecasting and resource planning: AI supports long-term energy demand forecasting and consumer-side energy use optimization.
Smart building energy systems: AI can manage HVAC, lighting, and other systems in commercial and residential buildings based on demand and energy pricing, reducing costs and environmental impact.
These applications show how AI is transforming traditional industries, introducing innovations that improve quality of life and operational efficiency.
Foundations of AI: Key Technologies Explained
The core of AI is machine learning, which enables systems to make decisions or predictions based on data analysis. At its heart lies the AI model, a mathematical representation of data. The model is built using algorithms trained on example datasets. The process begins with collecting relevant data, which is preprocessed (cleaned, missing values filled), followed by algorithm selection (e.g., linear regression). The model is trained to recognize patterns and make decisions. It’s then tested and optimized for accuracy. The more data provided, the better the model’s performance.
Deep Learning
Definition: An advanced form of machine learning using neural networks (analytical models inspired by the human brain) to detect complex patterns in large datasets.
Example use cases: Disease diagnosis from medical imaging, energy consumption forecasting, industrial machine failure prediction.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Definition: A subfield of AI focused on human-computer interaction through language. It allows systems to understand, analyze, and generate natural language.
Example use cases: Voice assistants like Siri or Google Assistant, automatic translation, speech recognition, and text-to-speech systems.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Definition: Advanced NLP models trained on massive datasets from the internet. These models understand context, answer questions, translate, and generate meaningful text.
Example use cases: ChatGPT, automated customer support, website chatbots, translation tools, article generation.
How to Use AI: Integrating Existing Models vs. Building Custom Solutions
AI can be implemented in two main ways: by integrating existing models or developing custom solutions. Each approach has its advantages, depending on business needs, resources, and goals.
Using pre-built models is faster, more cost-effective, and doesn't require deep technical knowledge. They offer easy integration via APIs and reduce the need for data collection or model training from scratch.
Examples of ready-to-use models:
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): For text generation, Q&A, translation, marketing content, and chatbots.
ResNet (Residual Networks): For image classification, object recognition, medical image analysis, and autonomous vehicle vision systems.
WaveNet: A speech synthesis model by Google that produces natural-sounding speech from text.
YOLO (You Only Look Once): Real-time object detection used in security, autonomous vehicles, and video analytics.
However, not all problems can be solved with pre-made models. In such cases, developing a custom AI model is necessary, especially for niche challenges that require tailored approaches. While more time- and resource-intensive, custom models provide competitive advantage by precisely addressing specific business needs. They offer better accuracy and full control over data and learning processes—crucial in industries requiring confidentiality and data security.
The decision between using pre-built models or creating custom solutions depends on factors like available resources, team expertise, data scope, and business goals. Hybrid approaches are also common—using both existing models and building specialized systems to maximize AI’s benefits.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is a powerful tool. When applied correctly, it can transform not just individual businesses but entire industries. With its wide range of benefits and applications, AI is a field worth investing in to unlock its full potential and reap long-term rewards.